This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Blocking "Hackers"
Definition of "Hacker"
For the purpose of this article, the term “hacker” refers to automated systems which attempt to login to your Synchronet TCP/IP servers and services using common, well-known, or randomly selected credentials (user names and passwords). These “hackers” are usually not humans sitting at keyboards and typing names and passwords but rather automated systems (e.g. scripts) which scan the Internet looking for systems with user accounts with guessable credentials and/or known vulnerabilities in their system software.
The Risk
The truth is, if one of these scripts successfully logged into your BBS as “root” or “admin” or whatever, they wouldn't know what to do: These scripts are most likely expecting to encounter some kind of Unix shell prompt with which they can further interrogate the system for known vulnerabilities or use the system to launch attacks against other hosts on your local network or the Internet. A Synchronet BBS command shell would not provide a favorable environment to these “hacking” scripts, but they don't know that, so they will just continue to blindly probe your ports and rattle your doorknobs. It may be irritating to some, but it's mostly harmless.
Synchronet's Defense
Synchronet normally disallows the use of common passwords by users (see the text/password.can file) and system operator accounts are protected with a secondary “system password”, so there should be little chance of a dictionary-based login attack actually succeeding. You can run exec/badpasswords.js (e.g. using jsexec) to check your user database for common passwords if you wish.
Synchronet also disallows the use of common administrative user login names (e.g. root, admin). This is accomplished through the text/name.can file.
To protect against “brute force” style attacks, that is, where an attacker may iterate through every possible password for a given user:
- Synchronet will delay a configurable amount of time before responding to failed login attempts (default: 5 seconds)
- Synchronet will throttle TCP/IP connections from attackers, increasing the configurable delay with each login failure (default: 1 second per failure)
- Create an entry in the
data/hack.logfile to notify the sysop operator(s) of the suspicious activity (default: after 10 failed login attempts) - Temporary ban (block connections) from an attacking IP address after a configurable number of failed login attempts (default: after 20 failed login attempts, duration: 10 minutes)
To do this, Synchronet tracks the source IP address of all failed login attempts. The sysop can list the failed login attempts:
- In the Synchronet Control Panel for Windows, using the View->Login Attempts... menu option
- In the Synchronet Console (sbbs), using the
a(show failed login attempts) command
Note:
- These IP addresses are only tracked during a single continuous invocation of the Synchronet process (rerunning the BBS clears the list and resets any temporary bans in effect)
- When a client successfully authenticates, its IP address is removed from the failed login list (if it exists there)
Auto-Blocking
To automatically block future connections from an IP address that has performed multiple consecutive failed login attempts:
- In the Synchronet Control Panel for Windows, set File->Properties->Security->Failed Login Attempts->IP Filter Threshold value...
... to a number you are comfortable with. I do not suggest setting this value lower than 10 so that you do not filter the IP address of valid BBS users who simply forgot their password. You may wish to warn your BBS users that they should not repeatedly attempt invalid passwords or their IP address may be automatically blocked by your system.
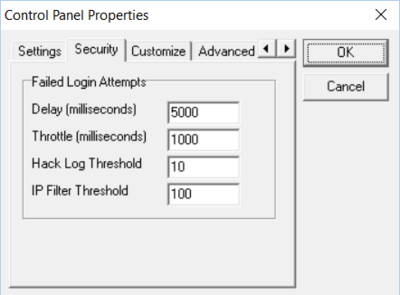
Note: These LoginAttempt values may be set in your sbbs.ini to different values for each Synchronet server/service if you wish, but that's a configuration that most sysops won't need.
See sbbs.ini for a list of all the failed-login-attempt related configuration settings available.