This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
SEXPOTS
Synchronet External Plain Old Telephone System (POTS) Support
Overview
Synchronet BBS Software version 3 was designed for client connections over TCP/IP protocols only (predominantly, Telnet). Over the 7 years since Synchronet v3's release, I've received occasional (but persistent) inquiries about the possibility or likelihood of adding modem support back into Synchronet to support direct analog dial-up users of the old BBS days before the Internet/broadband boom.
I've resisted this idea (for a few significant reasons I won't go into here), and have instead, suggested alternative methods of supporting dial-up users (e.g. running Synchronet v2.3 for DOS concurrently with v3, using *getty on Linux/Unix, using Manning's Dialup-to-Telnet Win32 gateway program with a front-end application, etc.). But these solutions all seemed insufficient in some ways or excessively complex or inconvenient. I wanted to provide something easier, more seamless.... “nicer”. Though I'm pretty sure there isn't much demand for dial-up BBSes today (30Kbps!), there has been enough interest from sysops to at least justify some effort (in my mind) to attempt to relive the BBS days of old, using actual *gasp* modems!
I knew exactly what was required to write a Serial↔TCP tunneling program and blogged on the www.synchro.net web-site way back in 2002 that I planned on writing just such a program to give dial-up capabilities to Synchronet v3 Win32 sysops.
Better late than never (?), I finally started writing this a program a few months ago (early 2007). I had to buy an analog modem (I'd thrown-out or donated all my modems years ago) and get a second phone line installed to test it, but finally, here it is: SEXPOTS (the name pays homage to SEXYZ).
While SEXPOTS was designed with Synchronet-Win32 sysops in mind, it should work with any TCP Server (e.g. Telnet BBS software).
I recently discovered a couple of unrelated Win32 programs by the name of COM2TCP which do fundamentally the same thing as SEXPOTS, but SEXPOTS is more robust/reliable, and has some niceties and cool BBS and Synchronet-specific features you'll like:
Features
- Can run from command prompt or as an NT service
- Handles modem initialization or “Null modem” connections
- Supports Telnet (with full option negotiation) or raw TCP connections
- Can accept “live” COM handles on the command-line (from “front-end” app)
- Caller-ID (CID) Support
- Optional Ident server to communicate CID information to TCP Server
- Telnet options used to communicate baud rate and CID info to TCP server
- Highly configurable (via
sexpots.inifile)
Distribution
SEXPOTS is freeware, licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) with portions licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL).
You can find the current source code (in C) in the Synchronet Git repository.
The latest and greatest build will be included in Synchronet-Win32 releases. You should be able to find/download the latest general release of SEXPOTS (sexpots.zip) at one or all of the following locations:
Command-line Syntax
Running sexpots -help will display the supported command-line usage (options and commands):
usage: sexpots [ini file] [options]
Options:
-null No 'AT commands' sent to modem
-com <device> Specify communications port device (or number)
-baud <rate> Specify baud rate for communications port
-live [handle] Communications port is already open/connected
-nohangup Do not hangup (drop DTR) after call
-host <addr | name> Specify TCP server hostname or IP address
-port <number> Specify TCP port number
-debug Enable debug log output
Additional options for Windows version:
NT Service Options:
-install install and enable NT service (SEXPOTS)
-service run as an NT service (background execution)
-remove remove NT service
-enable enable NT service (auto-start during boot)
-disable disable NT service
Additional options for Unix versions:
-syslog log to syslog rather than stdout/err
Install
No installation is required. You should be able to just run “sexpots”, optionally specifying command-line options to over-ride the default values (shown below), or the values in your sexpots.ini file (if you have one).
On Windows NT-based operating systems, you may install SEXPOTS as an NT service (runs in the background when your system boots up, before user login), by running sexpots -install. You can then start and stop the service using the “Services” Windows Control Panel applet or with the net start sexpots or net stop sexpots Windows command-lines. You can toggle the service start mode (between auto-start and disabled) with the -enable and -disable command-line options. When running as an NT service, the SEXPOTS log output goes to the “Application Log” in the NT event viewer.
Configure
Configuration is normally performed by editing the file sexpots.ini, located in the same directory where the SEXPOTS program (e.g. sexpots.exe) is located (e.g. exec). If sexpots.ini file doesn't exist or any of the key=value pairs are missing or blank in the file, the default values (indicated below) will be used.
Optionally, a different .ini file may be specified on the command-line (e.g. for running multiple concurrent instances of SEXPOTS on different COM ports). If an .ini file is specified on the command-line, it will be loaded after sexpots.ini (if the file exists), over-riding any settings in sexpots.ini.
Command-line options that modify values of the same name in the .ini file(s) will over-ride (take precedence over) the value in the .ini file(s).
The order of precedence for configuration values is (lower number is higher precedence):
- Command-line options
- Command-line specified
.inifile sexpots.ini(from same directory as executable)- Default values
The .ini files are just a plain text files that you can edit with any plain text/ASCII file editor (e.g. Windows notepad.exe or Unix vi). See ini files for more details.
Example .ini file (with default values given):
LogLevel = INFO ; set display/log output level Debug = FALSE ; enable debug logging (overrides LogLevel) PauseOnExit = FALSE ; wait for key-press on exit (non-service) CLS = FALSE ; send a form feed (clear screen) before copyright banner Prompt = PromptTimeout = 60 ; seconds to wait for a remote character after sending prompt (0=infinite) [COM] Device = COM1 ; COM port device name (or port number) BaudRate = 0 ; If non-zero, use this DTE rate (e.g. 115200) Hangup = TRUE ; Hang-up phone after call IgnoreDCD = FALSE ; Set to TRUE to ignore state of DCD DCDTimeout = 10 ; Seconds to wait for DCD to drop DTRDelay = 100 ; Milliseconds to delay before hangup NullModem = FALSE ; Set to TRUE to not send AT commands to modem Parity = FALSE ; Use parity (error detection/correction) bit ParityOdd = FALSE ; Use odd (not even) parity for parity calculations ByteSize = 8 ; Number of data bits per byte StopBits = 1 ; Number of stop bits per byte [Modem] Init = AT&F ; Modem initialization string AutoAnswer = ATS0=1 ; Put modem into "auto-answer" mode CleanUp = ATS0=0 ; When exiting, turn off auto-answer EnableCallerID = AT+VCID=1 ; Enable Caller-ID support (or try AT#CID=1) Timeout = 5 ; Seconds to wait for a response from modem ReInit = 60 ; Minutes of inactivity while waiting for caller before re-initialization Answer = ATA ; Answer command Ring = RING ; Ring indication (from modem) ManualAnswer = FALSE ; Set to TRUE to disable auto-answer and use ring detection/manual answer instead [TCP] Host = localhost ; Hostname or IP address of TCP server Port = 23 ; TCP port number of TCP server NoDelay = TRUE ; Set to TRUE to disable the Nagle Algorithm Telnet = TRUE ; Set to FALSE to disable Telnet mode [Telnet] Debug = FALSE ; Set to TRUE to log Telnet commands sent/recv AdvertiseLocation = FALSE ; Set to TRUE to send "WILL SEND LOCATION" TermType = SEXPOTS ; You shouldn't normally change this value TermSpeed = 28800,28800 ; Default terminal speed reported (tx, rx bps) [Ident] Enabled = FALSE ; Set to TRUE to enable Ident (RFC1413) server Port = 113 ; TCP Port Ident server will listen on Interface = 0 ; IP address of network interface (0=Any) Response = CALLERID:SEXPOTS ; Resp-type and Add-info portions of response
Note: SEXPOTS v1.25 and earlier did not supports comments on .ini string value lines as shown above. As of v1.26 (and later), string values (e.g. com device name, modem strings, hostname, etc.) are terminated at the first white-space character so white-space characters are not permitted in the string values of the SEXPOTS .ini file.
Note: Support for the [modem] ReInit key was added in SEXPOTS v1.27.
Prompting for a TCP Host
By setting the Prompt key value (to a text string asking the remote user to press a key), you can have SexPOTS connect to one of a set of TCP hosts by creating additional [TCP:x] sections in your .ini file, where x is a single non-control character that the user may respond with to choose that host to connect with. If the user does not respond by the configured PromptTimeout duration (default: 60 seconds) or responds with an invalid key press, the default host is connected to.
Example .ini file (with default values given):
Prompt: "Hit 'P' for PBX or ENTER for BBS now" [TCP] Host=mybbs Port=23 Telnet=true [TCP:P] Host=thepbx Port=2600 Telnet=false
NT Service Control
If installed as an NT service, SEXPOTS can be started and stopped using the “Services” applet from the Windows Control Panel (usually found under “Administrative Tools”) or by using the Windows NT command-line tools sc.exe or net.exe.
Examples:
sc start sexpots
sc query sexpots
sc stop sexpots
net start sexpots
net stop sexpots
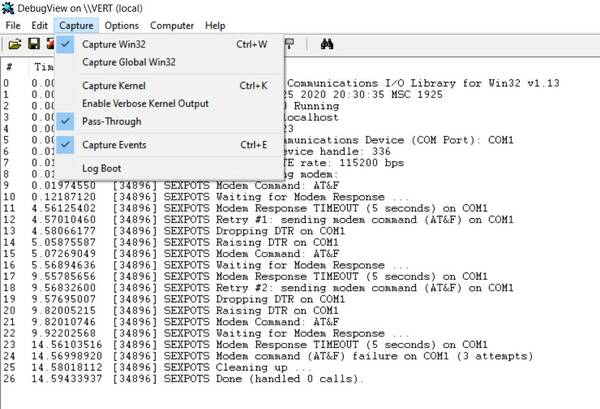
DebugView
When running SEXPOTS as an NT Service, you may want to use a debugger viewer (e.g. DebugView, run as Administrator) to see the detailed log messages:
Notes on Advanced Features

SEXPOTS will report the connection (DCE) rate to a Synchronet Terminal Server using the Telnet “TERMINAL SPEED” sub-option. Synchronet will use the reported speed to calculate estimated file transfer durations, update the node record, log to the user logon list, and save in the user record as the user's most recent “connection type”.
SEXPOTS can report Caller-ID information to the Synchronet Terminal Server using the Telnet “Location” option. Synchronet will store the Caller-ID reported Phone Number in the user's 'note' field (where the IP address is normally stored) and the Caller-ID reported Caller Name in the user's 'computer' field (where the Hostname is normally stored). Synchronet will also log each caller's Caller-ID information for record-keeping purposes.
Alternatively, SEXPOTS can report the Caller-ID information using the Ident protocol, but this feature is disabled by default and is not the preferred mechanism (use the Telnet “Location” option instead).
Using Synchronet v3.14a or earlier, the Synchronet Terminal Server will detect the caller as just another Telnet connection, but coming in from the local network interface (IP address).
Linux/Unix Version
There is a *nix port of SEXPOTS in Git.