Table of Contents
FTP Server
The Synchronet FTP Server is a native server (written in C) which supports the FTP and FTPS TCP protocols for file transfer.
Anonymous Logins
So-called “Anonymous FTP” logins (client-login using the user-ID “anonymous”, “ftp”, or “guest”) are supported when the BBS user database contains a “Guest” user account.
Traditionally, the user's email address is given as the password during “anonymous FTP” logins. To block specific email addresses from being used in this manner, add the address(es) to your text/email.can file.
Sysop Access
To login with system operator access, the user must login with a user account that has a security level of 90 or higher and provide a password of “<user-pass>:<sys-pass>” where <user-pass> is the user's personal password and <sys-pass> is the system password as configured in SCFG->System.
A successful sysop login will generate a login message stating “Sysop access granted”.
230-Sysop access granted.
Logging in with just a personal password will give the user/sysop normal (non-sysop) access.
Sysop access allows the FTP user to mount local file systems and execute administrative commands via the FTP server.
When logged-in with sysop access, the user has access to the following additional FTP commands:
SMNT SITE EXEC
Local File System Access
Local file system access is enabled by default. Local file system access can be disabled with the NO_LOCAL_FSYS Options flag in the [FTP] section of the ctrl/sbbs.ini file or by un-checking the “Local File System” checkbox in the Synchronet Control Panel->FTP->Configure dialog.
When local file system access is enabled, a user with sysop access can “mount” a local file system using the FTP CWD or XCWD commands to change to “local:<path>” where <path> is the local file system directory to mount. An alternative method of mounting the local file system is to use the SMNT <local-dir> command. To re-mount (switch back to) the BBS file system, the SMNT bbs: command can be used or CWD/XCWD command with a path beginning with bbs:.
Configure
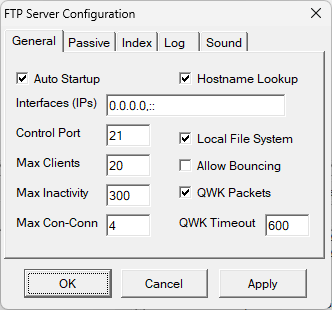
The Synchronet FTP server can be configured via SCFG:Servers->FTP Server:
╔══════════════════════════════════════════════╗ ║ FTP Server ║ ╠══════════════════════════════════════════════╣ ║ │Enabled Yes ║ ║ │Log Level Informational ║ ║ │Network Interfaces 0.0.0.0, :: ║ ║ │Control Port 21, Data: 20 ║ ║ │Passive Interface (IPv4) 0.0.0.0 ║ ║ │Passive Port Range 1024 - 65535 ║ ║ │Auto-generate Index File 00index ║ ║ │QWK Message Packet Transfers Yes ║ ║ │QWK Message Packet Timeout 10 minutes ║ ║ │Max Clients 100 ║ ║ │Max Inactivity 5 minutes ║ ║ │Max Concurrent Connections Unlimited ║ ║ │Sysop File System Access Yes ║ ║ │Allow Bounce Transfers No ║ ║ │Lookup Client Hostname Yes ║ ║ │Failed Login Attempts... ║ ╚══════════════════════════════════════════════╝
... via SBBSCTRL:FTP->Configure:
... or via manual editing of the [FTP] section of the ctrl/sbbs.ini file.
sbbs.ini
The [ftp] section of the ctrl/sbbs.ini file supports the following configuration settings (key = value lines):
| Key | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AutoStart | true | Automatically start up the server (manual is only supported in sbbsctrl) |
| Interface | [global] | Comma-separated list of IPv4 and IPv6 network interfaces to listen on for incoming TCP connections |
| Port | 21 | Control TCP Port |
| MaxClients | 10 | Maximum number of simultaneous incoming TCP sessions supported |
| MaxConcurrentConnections | 0 | Maximum number of concurrent connections from the same IP address (0 = unlimited) |
| MaxInactivity | 300 | Maximum amount of TCP session inactivity before timeout and disconnection (in seconds) |
| QwkTimeout | 600 | Maximum amount of time to wait for QWK packet creation (in seconds) |
| SemFileCheckFrequency | [global] | Frequency (in seconds) of checks for semaphore files |
| MinFileSize | 0 | Minimum uploaded file size, in bytes (0 = no-minimum) |
| MaxFileSize | 0 | Maximum uploaded file size, in bytes (0 = no-maximum) |
| PasvIpAddress | 0 | IPv4 address to advertise for PASV client data connections (0 = auto) |
| PasvPortLow | 1024 | Lowest TCP port number to use for PASV data connections |
| PasvPortHigh | 65535 | Highest TCP port number to use for PASV data connections |
| HostName | [global] | DNS Hostname of server |
| IndexFileName | 00index | Filename to use for auto-generated downloadable file listings |
| AnswerSound | WAV file to play (on Windows) when answering incoming connections | |
| HangupSound | WAV file to play (on Windows) when clients disconnect | |
| HackAttemptSound | WAV file to play (on Windows) upon detected suspected hack attempt | |
| TempDirectory | [global] | Directory to use for temporary file storage |
| LogLevel | [global] | Minimum severity of log messages to be displayed / stored |
| BindRetryCount | [global] | Maximum number of TCP port bind attempts before failure |
| BindRetryDelay | [global] | Delay (in seconds) between TCP port bind retries |
| LoginAttempt* | [global] | Failed login attempt throttling / filtering / banning |
| Options | ALLOW_INDX_FILE | ALLOW_QWK | FTP server option flags (see below for details) |
Options
The Options key of the [ftp] section of the ctrl/sbbs.ini file supports the following option flags (separated by a | character):
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| DEBUG_RX | Log all received commands (Debug log level) |
| DEBUG_TX | Log all transmissions (Debug log level) |
| DEBUG_DATA | Log all DATA channel activity |
| INDEX_FILE | Auto-generate index (listing) files for optional download |
| ALLOW_QWK | Allow download/upload of QWK/REP packets |
| ALLOW_BOUNCE | Allow authenticated non-guest/anonymous users to use FTP Bounce (FXP) functionality - not recommended |
| NO_LOCAL_FSYS | Disable local file system access (for sysops) |
| KEEP_TEMP_FILES | Don't delete temporary files, for debug purposes |
| LOOKUP_PASV_IP | Resolve public IP address for PASV response |
| NO_FTPS | Disable AUTH TLS support - not recommended |
| NO_HOST_LOOKUP | Do not resolve/log hostnames of incoming TCP connections |
| NO_RECYCLE | Do not allow this server to be automatically recycled by external event |
| MUTE | Disable all sound (WAV) files from playing |
Aliases
You can create a list of file aliases that will appear in your FTP root directory for:
- Quick and easy access to often downloaded user files
- Static filenames that corresponds to a dynamically changing filenames
- Download access to files on the local disk not in the BBS file database
Edit the file ctrl/ftpalias.cfg with a text editor (SBBSCTRL->FTP->Edit->Filename Aliases).
The ftpalias.cfg file format is one file or directory alias per line, in the form:
<alias> <path> [description]
The <alias> field is not case-sensitive and may not contain spaces. This is the filename that will appear in listing of your FTP root directory.
The <path> field is either the full path and filename to a file on a
local file system (e.g. C:\DOCS\MYFILE.TXT or /docs/myfile.txt) or a virtual path to a file in the
BBS file database. Virtual paths are specified as
bbs://lib/dir/filename
where lib is the library short name, dir is the directory internal code and filename is the actual filename of the referenced file (may be the long filename, but may not contain spaces).
The [description] field is the optional description of the file that will be used in the dynamically generated Auto Index file (if you have this option enabled). Descriptions of “hidden” indicate files or directories that are not be included in listings.
Blank lines are ignored.
Lines beginning with a semicolon (;) character are considered comments and are ignored.
Example Alias:
sbbs_for_dos.zip bbs://main/sbbs/sbbs230b.zip Current version for SBBS for DOS
Display Files
The Synchronet FTP server can optionally send text files from your text directory to the FTP client/user under certain conditions:
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
ftplogin.txt | Sent before the username and password is requested |
ftphello.txt | Sent upon successful login |
ftpbadlogin.txt | Sent upon unsuccessful login attempt |
ftpbye.txt | Sent upon logoff (before server acknowledgment of the QUIT command) |
Supported Commands